
Eligible businesses can have access to a range of business concessions based on the aggregated turnover test.
The aggregated turnover test
The small business entity (SBE) aggregated turnover test is used to determine a business’s eligibility for a range of tax concessions. The test requires the annual turnovers of the business and its affiliates and any entities connected with it (if any) to be aggregated.
However, the applicable turnover threshold varies depending on the particular tax concession. For example:
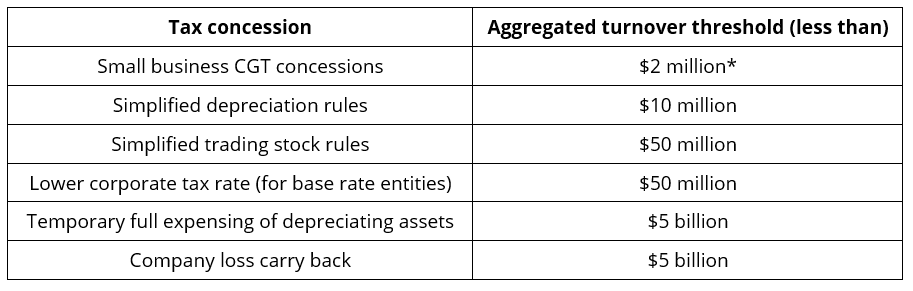
* The $6 million maximum net asset value test is an alternative test to the $2 million turnover test.
The ATO recently issued one Taxation Determination, three Draft Taxation Determinations and an Addendum to a Law Companion Ruling discussing aspects of the SBE aggregated turnover test.
According to the ATO, the relevant income year for calculating aggregated turnover is the income year of the business claiming the tax concession (ie the taxpayer) – thus only the annual turnovers of entities that are affiliates or entities connected with the taxpayer for the period that matches the taxpayer’s income year are included.
Example
Suppose the taxpayer has a 30 June year-end while an entity connected with the taxpayer has a 31 December year-end. In that case, the entity’s annual turnover connected with the taxpayer will have to be calculated as if it were a June balancer.
As regards qualifying for the 25% corporate tax rate, the relevant year for calculating a company’s aggregated turnover is the income year in which its status as a base rate entity is determined. The entity’s aggregated turnover for any earlier income year is irrelevant for this purpose. However, for franking purposes, the aggregated turnover for the income year immediately prior to the year in which the tax rate is being determined is instead used to determine the company’s franking rate.
Talk to our KMT tax adviser about the tax concessions available to your business.
Fuel tax credits: Getting your claim right
Fuel tax credits provide businesses with a credit for the fuel tax (excise or customs duty) that’s included in the price of fuel used in:
- Machinery
- Plant and equipment
- Heavy vehicles
- Light vehicles travelling off public roads or on private roads.
The amount depends on when you acquire the fuel, what fuel you use, and the activity you use it in. Fuel tax credits rates also change regularly, so it’s important to check the rates each time you prepare your business activity statement (BAS).
Some fuels and activities are not eligible, including fuel you use in light vehicles of 4.5 tonnes gross vehicle mass (GVM) or less, travelling on public roads.
The ATO states that the easiest and safest way to get fuel tax credit claims right is to use:
- The simplified methods – such as the basic method for heavy vehicles, which provides certainty and protection for claims less than $10,000 each year;
- A global positioning system (GPS) or telematics technology product with a current product ruling provides certainty, regardless of the size of the claim, provided the product is used as set out in the product ruling.
Small business tax offset
A sole trader, an individual who is a partner in a partnership or an individual who is a beneficiary of a trust may qualify for the small business tax offset if the sole trader, partnership or trust qualifies as a small business entity (total annual turnover less than $10m). The offset is not available to an individual acting as a trustee of a trust. Personal services income is also not eligible for small business income tax offset.
The rate of the offset was 8% up to the end of the 2019-20 income year, but increased to 13% for 2020-21 and will again increase to 16% for 2021-22 and then remain at that level. The ATO calculates the offset using information from the business’s tax return, with the offset amount shown on the notice of assessment.
Taxable payments annual report
Businesses and government entities who make payments to contractors may need to report these payments and lodge a Taxable payments annual report (TPAR).
Contractors can include subcontractors, consultants and independent contractors. They can operate as sole traders (individuals), companies, partnerships or trusts.
A TPAR must be lodged by 28 August each year.
Our KMT tax adviser can advise whether you are eligible to claim fuel tax credits and can help you claim credits.
The article is provided for general information purposes only and is not intended as professional advice. Readers should not act on the information contained therein without professional advice from a suitably qualified accountant.


